Facing the problem of what to do with rubbish in your town or region? Thermal treatment processes can turn waste into energy and other useful by-products. This article explores different ways we can manage waste, helping us make smarter choices for the environment.
Keep reading to find out more.
Key Takeaways
- Thermal treatment changes rubbish into energy and other useful things. Methods like incineration, pyrolysis, and gasification break down waste with heat.
- These processes need careful handling to reduce harmful emissions like dioxins and heavy metals that can harm our health.
- Innovations in waste management aim to make these treatments cleaner and more efficient. New technologies could help recycle materials better and reduce environmental impact.
- Following the waste hierarchy is important. It tells us to prevent wastage first, then recycle, before considering thermal treatment options for managing solid waste responsibly.
Understanding Thermal Waste Treatment

Thermal waste treatment involves heating rubbish to break it down or turn it into energy. It plays a big part in managing solid waste, keeping our cities clean and reducing the trash that ends up in landfills.
Waste Hierarchy
The waste hierarchy puts recycling and waste prevention at the top. This means we should always try to use less and recycle more before thinking about other options like burning or burying waste.
It’s a simple but powerful guide for reducing our environmental impact. By following this order, we can cut down on harmful gases from landfills because we’re not just throwing everything away.
Next in line after recycling is energy recovery methods, which include turning waste into power or heat through processes like incineration. Only as a last resort should we consider disposal methods such as landfilling, which can release methane gas—a potent greenhouse gas—into the atmosphere.
Understanding and applying the waste hierarchy correctly helps us make smarter choices that protect the planet while managing trash efficiently. Let’s explore how thermal treatment fits into this approach by looking at various processes used to manage solid garbage.
C02 Emissions and Decarbonization
Moving from the waste hierarchy, we tackle CO2 emissions and decarbonisation—a critical step for sustainable waste management. The use of thermal treatment in managing solid refuse significantly impacts our carbon footprint.
Incineration plants, while effective in reducing waste volume, release toxic pollutants, including CO2 into the atmosphere. Not all outcomes are negative; advancements like thermal plasma technology show promise in cutting down these emissions by breaking down hazardous components more safely.
Decarbonising the process involves capturing valuable resources like heavy metals and converting waste to energy instead of letting it sit in landfills. Thermal treatments can transform refuse into less harmful substances such as benign vitrified slag or provide heat for district warming systems.
This shift not only reduces greenhouse gases but also embraces a cleaner, more sustainable method of handling what we discard. Through careful innovation and choosing greener technologies, we make strides towards a less polluted world while still addressing our growing waste problem.
The Importance of Thermal Treatment in Waste Management
Thermal treatment plays a key role in managing waste. It changes waste into something useful and reduces how much there is. This process uses heat to make waste safe and turn it into stable products that can be used again.
For example, using thermal processes helps break down the organic parts of city rubbish fast.
This method also helps prevent heavy metals from leaking from the soil by changing the soil’s physical and chemical traits. Thermal plasma technology is great for getting rid of dangerous waste toxins effectively.
Plus, incinerating waste can recover energy and cut down on rubbish size, even though it might release harmful pollutants. So, thermal treatment is crucial for both sanitising rubbish and creating valuable end-products.
Different Thermal Treatment Processes for Solid Waste
Turning solid waste into useful energy and materials involves several heat-based methods. Each process, from burning rubbish in giant ovens to breaking it down with high-tech plasma beams, transforms trash into power, gas, or other valuable products.
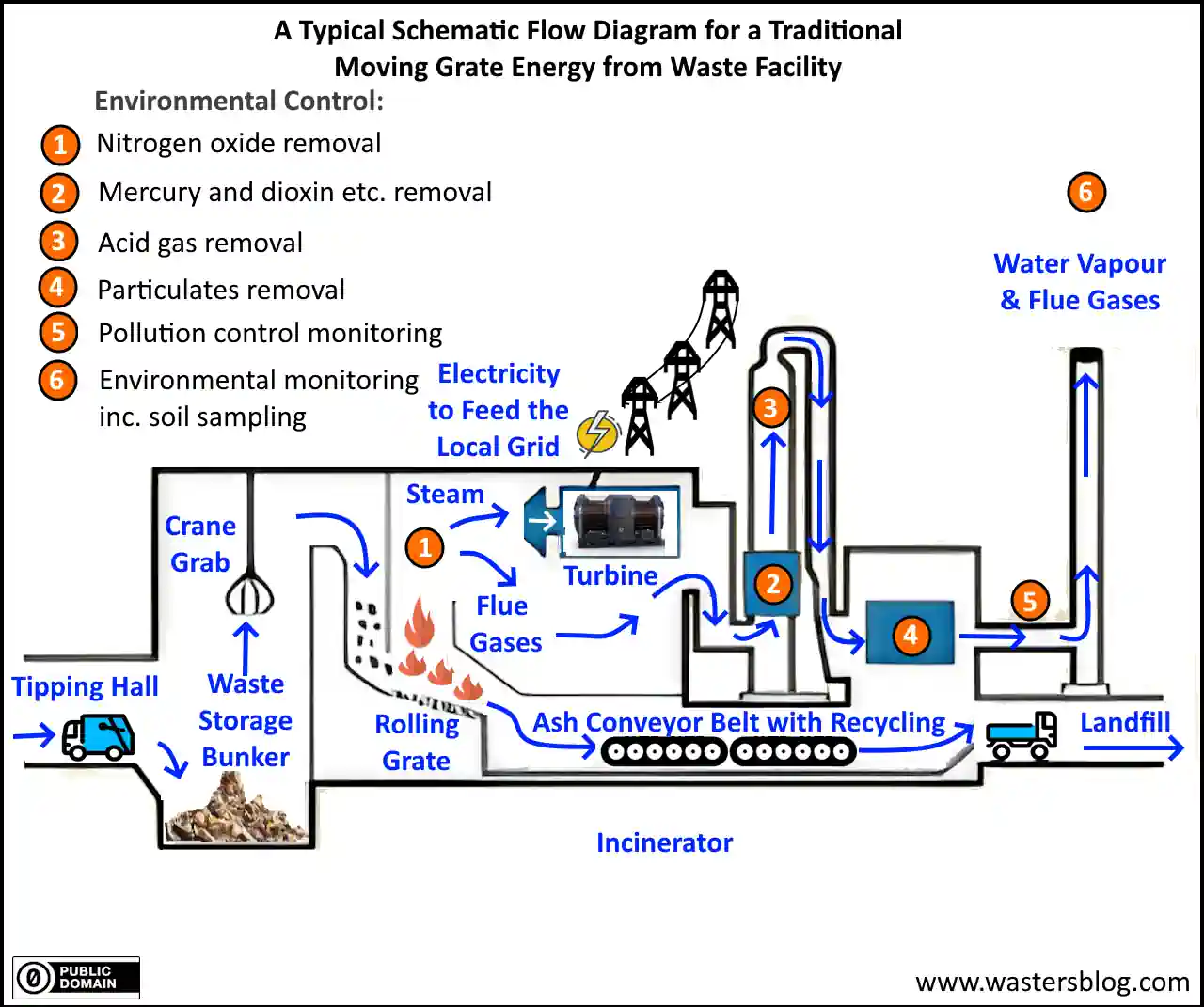
1. Incineration
Incineration burns waste, turning trash into ash, steam, and gases. This method greatly reduces the volume of solid materials, by up to 90%. It’s like watching a magic trick in which bulky items disappear right before your eyes! At home, I’ve seen how even quite large amounts of garden waste can quickly turn to just a handful of ash after burning.
The heat generated can also create electricity or heat nearby buildings. Yet, this process isn’t all smoke and mirrors. It releases harmful toxins into the air—dioxins and heavy metals like mercury that we absolutely must handle with care.
This method has its dark side with the release of toxic substances such as dioxins and mercury fumes. These pollutants require advanced scrubbers and filters in incinerators to capture them before they escape into our air.
So while we get rid of heaps of garbage efficiently and extract energy, ensuring clean operation is key for our health and planet’s wellbeing.
Next up: exploring Pyrolysis transforms waste under high temperatures without oxygen.
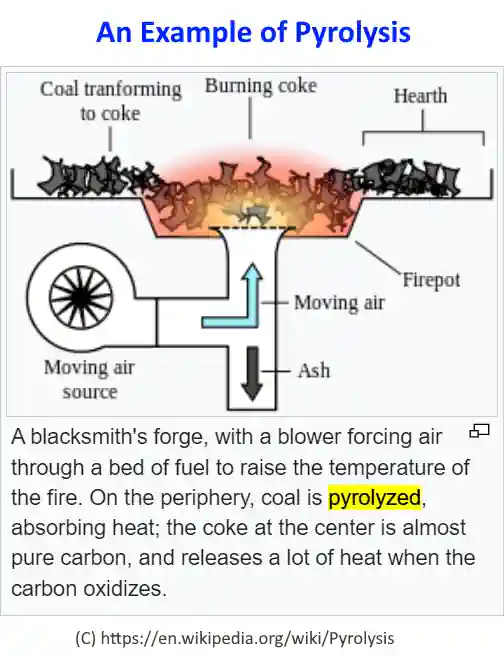
2. Pyrolysis
Moving from incineration, pyrolysis offers a different approach to managing solid waste. This process heats up organic materials without oxygen, breaking them down into simpler substances.
It not only reduces the volume of rubbish but also lessens its environmental impact. By doing so, pyrolysis turns waste into useful products like syngas, charcoal, and oils that can be used to generate energy or as raw materials for various industries.
Pyrolysis stands out as a green option in waste management plans. Its ability to process mixed municipal garbage and medical refuse without emitting harmful gases makes it a sustainable choice.
The method is ideal for producing clean energy from rubbish while also tackling the growing problem of waste accumulation worldwide. Through this thermal decomposition technique, we’re able to recover valuable resources buried in landfills and put them back into circulation—truly turning trash into treasure.
3. Gasification
Gasification turns solid waste into useful energy with very high heat and a small amount of oxygen. This process changes waste materials into gas, water, and ash without burning them completely.
It’s different from traditional methods because it can work with many types of waste, like heavy oil or even used car tyres. I’ve seen this method create less air pollution compared to others, making it a cleaner choice.
In my time observing these processes, gasification stood out for its ability to make synthetic gas from things we usually throw away. This gas can then be used to generate electricity or produce both chemicals and fuels.
Plus, the leftover ash is often safe enough to use in construction materials. With careful control of temperature and oxygen levels, this approach cuts down on harmful emissions significantly.
4. Plasma Gasification
Plasma gasification uses a plasma torch to turn waste into gas at very high temperatures. This process works well with many types of rubbish, including things that are usually hard to get rid of.
It turns these wastes into useful gases like hydrogen and methane, as well as solid materials such as slag and ash. The magic lies in the plasma’s intense heat and the low oxygen environment, which breaks down waste without burning it.
This method is great for dealing with dangerous wastes safely and effectively. Not only does it reduce harmful substances, but it also creates new resources from what was once considered trash.
Plasma gasification stands out because it can handle both non-hazardous and hazardous materials, making it a versatile solution in modern solid refuse management.
Importance of Low Water Content Waste Drying
Waste drying plays a key role in preparing solid waste for further thermal treatment. This process reduces moisture in the waste, making it easier to handle and more efficient for energy recovery.
Waste drying ensures that wet garbage dries out properly before moving on to other stages like burning or gasification.
Drying helps cut down greenhouse gas emissions by lightening loads and enhancing combustion efficiency. It turns bulky refuse into denser, fuel-like material ready for conversion into energy or recycled goods.
Environmental Impacts and Considerations of Thermal Waste Treatment
Thermal treatment can create dangerous fumes like dioxins and gases such as mercury and cadmium. These are really bad for our health and can cause cancer.
In our typical schematic (see above), we have listed the important environmental controls that every energy-from-waste (EfW) facility should provide.
Using heat to manage waste, in incinerators, does more than just shrink piles of rubbish. It turns some of the trash into energy and new materials like ash or slag, which we can use again in different ways.
However, laws see ash from burning city rubbish as risky stuff that needs safe handling before we can do anything else with it.
Technologies that use plasma show promise because they’re good at getting rid of nasty bits in hazardous waste without leaving much behind that could harm us or our planet.
Future Innovations in Thermal Waste Treatment
Innovations in thermal waste treatment are key to making solar PV panel recycling better. Experts are looking into microwave thermal technology for its benefits. It uses less energy and is quicker than other methods.
This approach is often also cheaper and can be done right where the waste is found.
Gasification and pyrolysis, two methods that use very hot conditions with little oxygen, will see major upgrades. They already have fewer harmful emissions than most treatments. Research aims to make them even cleaner and more efficient at breaking down waste into useful products like fuel or chemicals.
Thermal Treatment Process Article Conclusion
Exploring thermal treatment for solid waste opens new avenues for managing rubbish. These methods, like heating waste without oxygen, and turning trash into gas using plasma technology, make disposing of garbage efficient.
They bring benefits such as reduced emissions and the creation of valuable by-products. This approach is not only practical but also impactful on both a local and global scale.
For those keen to dive deeper into this topic, many resources complement what we’ve discussed here. They offer insights into cutting-edge practices in waste management technologies.
We stand at a critical point where choosing sustainable disposal methods can significantly affect our environmental footprint. Let’s commit to solutions that safeguard our planet for future generations.
Engaging with these technologies today paves the way towards a cleaner, more sustainable world tomorrow.
FAQs
1. What exactly is thermal treatment of waste?
Thermal treatment of waste involves using high temperatures to decompose, sterilise, or convert solid waste into energy or other useful products. This process can tackle various wastes, including municipal solid waste (MSW), medical waste, and chemical waste.
2. How does incineration work in managing solid waste?
Incineration burns the organic components found in solid waste at high temperatures. The process reduces the volume of the material and can generate energy from the heat produced. It also deals with flue gases and particulates through pollution control technologies to minimise environmental impact.
3. Can you tell me about pyrolysis and its role in recycling technology?
Pyrolysis heats up carbonaceous materials like plastics without oxygen to break them down into pyrolysis oil, gas, and coke. It’s a promising recycling technology that turns hard-to-recycle plastics into valuable commodities while reducing landfill reliance.
4. What’s plasma arc gasification?
Plasma arc gasification uses an ionised gas called plasma to turn organic material into synthetic gas (syngas) and slag—a type of glassy residue—under very high temperatures. It’s an advanced form of thermal treatment that can manage mixed or hazardous wastes while producing clean energy.
5. Are there any sustainable benefits to thermal treatment processes for solid waste management?
Yes! Thermal treatments such as incineration and plasma arc gasification not only reduce the volume of landfilled trash but also recover energy—converting what was once ‘waste’ into electricity or natural gas for heating homes… Plus, they help cut down on fossil fuel usage by creating renewable energy sources from what we throw away.
6. How do these processes handle emissions and pollutants?
Modern thermal treatment facilities are equipped with advanced pollution controlling systems designed to capture harmful emissions like volatile organic compounds, particulate matter, carbon monoxide—and even neutralise acidic gases before they’re released into our atmosphere… ensuring a cleaner environment.
THE FOLLOWING IS ARCHIVE CONTENT FROM OUR ORIGINAL 2011 ARTICLE:
Thermal Treatment of MSW in Grimsby (Newlincs Incinerator)
Thermal treatment of MSW is the single most popular form of municipal waste disposal, and Grimsby’s Energy from Waste plant takes 80,000 tonnes of the area’s waste and has done so since 2005.
Before we start, let’s be sure we know what we are talking about here:
Definition of Thermal Treatment
Thermal treatment is any waste treatment technology that involves high temperatures in the processing of the waste feedstock. Commonly, this involves the combustion of waste materials. – via Wikipedia
The Grimsby Incinerator, Stallingborough appears to continue in operation (Autumn 2018 update).
Back in 2011, we published the Newlincs Press Release about the Grimsby thermal treatment of waste facility. We continue to include that article below:
Aecomm Press Release August 2011:
It’s a combined heat and power energy from waste (EfW) plant (Thermal Treatment Facility) by Earth Tech (Now Aecom), and located at Stallingborough on the Humber bank near Grimsby. This was part of a £21 million integrated waste management facility (IWMF) built for Newlincs Development, the waste management contractor for North East Lincolnshire County Council.

Newlincs is a special purpose company which was set up by Cyclerval (UK) and its parent company, TIRU SA, to run the 25-year concession contract for recycling and disposal of the approximate 80,000 tonnes per annum of municipal and domestic waste arising from the 1 60,000 households within the council area.
The EfW plant provides thermal treatment for municipal solid waste (MSW) as part of an integrated waste management scheme for the area, which also includes kerbside collection, community recycling centres, bring sites and green waste composting. The IWMF site at Stallingborough also has provision for composting facilities and a storage depot for recovered materials for onward transport to recycling centres.
Up to 56,000 tonnes of municipal and household waste is processed each year by the plant and there is a condition in the planning consent that limits the waste to be treated at the plant to that arising only from the North East Lincolnshire Council area. Heat output (in the form of high-pressure hot water) and approximately 3MW of electrical power are transferred from the EfW plant to a neighbouring industrial process and manufacturing plant. In this way, the facility provides a local solution to the council’s waste recycling and disposal needs while providing a particular benefit to a local manufacturing plant and the wider local community.
In May 2000 Newlincs appointed Earth Tech as the preferred bidder for the design and build contract for the EfW plant. Following the financial closure in December 2001, Earth Tech was awarded the turnkey construction contract for the scheme.
The simple and robust design makes for an economically attractive thermal treatment system with an average availability of over 90%.
In designing the plant, the objective was the delivery of a capital cost-effective plant with the virtues of easy maintainability and a 25-year design life.
Copyright of MSW Thermal Treatment Incinerator Image: By Alan Murray-Rust, CC BY-SA 2.0, Link
Copyright of Edmonton Incinerator image: CC BY-SA 2.0 by Fin Fahey





