Landfill tax rules puzzle many UK businesses and residents. People often ask, “Who pays landfill tax?” The answer matters because this tax affects waste disposal costs for everyone, from small shops to large companies.
Getting it wrong can lead to hefty fines and legal troubles.
The UK government started landfill tax in 1996 to cut waste and boost recycling. This tax now stands as one of the main tools to push businesses toward greener waste choices. The rates keep rising each year, making proper waste management more vital than ever.
We'll break down the facts about landfill tax rates for 2025, who needs to pay, and how to handle it right. You'll learn about standard rates, lower rates for special materials, and ways to save money through proper waste sorting.
Ready to master the basics of UK landfill tax? Let's explore the details.
Key Takeaways
- Landfill site operators pay the tax directly to HMRC, with standard rates rising to £126.15 per tonne in 2025 for active waste.
- The tax started in 1996 under John Gummer's leadership and uses two rates: a standard rate for most waste and a lower rate of £4.05 per tonne for qualifying materials like soil and rocks.
- Special exemptions exist for pet cemeteries, military forces, mining waste, and dredged materials from waterways, helping these sectors manage costs while protecting the environment.
- The tax has pushed UK businesses to boost recycling efforts. Many firms now use energy-from-waste facilities instead of the country's 500 active landfill sites.
- Local councils and waste producers must factor these taxes into their disposal fees. The system helps fund green projects while creating new jobs in Britain's recycling sector.
What is Landfill Tax?

The UK government started landfill tax in 1996 under John Gummer's leadership. This tax makes people pay extra money to dump waste in landfills. The main goals focus on cutting down waste and pushing more recycling efforts across Britain.
Landfill tax serves as a vital tool in our fight against waste, encouraging better choices for our environment – John Gummer, Former Secretary of State for the Environment
The tax system works with two rates: a standard rate for most rubbish and a lower rate for less harmful materials. Every waste company must pay this tax on top of their normal dumping fees, plus VAT.
Most businesses pass these costs to their customers through higher service charges. The next section explains who needs to pay these taxes and what rates apply in 2025.
Who is Responsible for Paying Landfill Tax?
Landfill site operators must pay tax on all waste they accept at their sites – this includes both active and inactive materials. Local councils and businesses need to factor these costs into their waste disposal fees, which often leads to higher charges for waste collection services.

Landfill site operators
Licensed landfill site operators must pay tax on waste they accept at their sites. These operators need proper permits under the Environmental Permitting Regulations 2016 for England and Wales.
Each operator must register with HMRC before accepting any waste materials at their facilities.
Site operators track all waste types entering their facilities through detailed records. They calculate tax rates based on whether materials fall into standard or lower rate categories.
The operators must follow strict rules about waste acceptance, storage, and disposal methods to stay compliant with environmental regulations.
The legal responsibility extends beyond just the main operators. Site controllers share joint liability for landfill tax payments if the primary operator isn't directly involved in waste management activities.
This rule ensures proper tax collection and environmental protection across UK waste disposal sites. The next section explains the role of waste producers and local authorities in the landfill tax system.
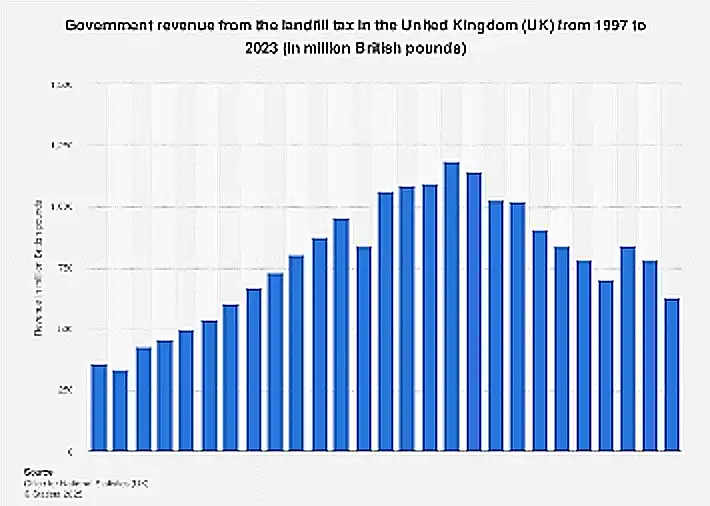
“UK: annual landfill tax revenue 2023 …” from www.statista.com and used with no modifications.
Waste producers, including businesses and local authorities
Businesses and local authorities stand at the front of waste production in the UK. These waste producers must pay fees to licensed landfill operators, who then pass the landfill tax to HMRC.
Local councils handle most household waste disposal through their waste collection services. Many companies now focus on recycling and resource recovery to lower their tax costs.
The landfill tax serves as a key driver for sustainable waste management practices across the UK – Environmental Protection Agency
Manufacturing firms, construction companies, and retail businesses create large amounts of solid waste each day. The tax rates push these groups to find better ways to handle their waste.
Most firms now sort their materials between active and inactive waste to save money. The next section explains the exact rates these groups must pay in 2025.
Landfill Tax Rates in 2025
The UK landfill tax rates will see a sharp rise in 2025, pushing businesses to rethink their waste management plans. The standard rate targets active waste materials – like household rubbish and construction debris – while lower rates apply to inactive waste such as rocks and soil.

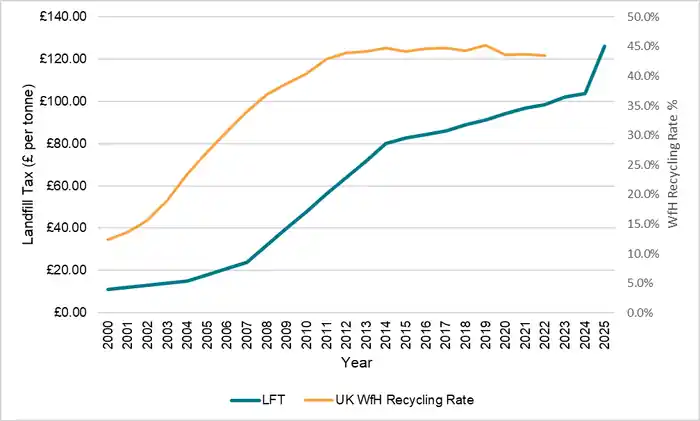
“Landfill Tax Soars to £126.15 Starting …” from affordablewastemanagement.co.uk and used with no modifications.
Standard rate
Landfill tax rates in the UK follow a clear standard rate structure for most waste materials. Local councils and waste management companies must pay £126.15 per tonne in 2025 for active waste disposal at landfill sites.
This rate marks a steady rise from previous years, where operators paid £96.70 in 2021 and £94.15 in 2020.
Waste producers face strict rules about proper waste classification under the Environmental Protection Act 1990. Active waste includes items like household rubbish, construction debris, and hazardous materials that need careful handling at landfill disposals.
These materials create higher environmental risks through greenhouse gas emissions and potential habitat destruction.
Many local authorities now focus on sustainable waste management to reduce their tax burden. They push for more recycling, reuse of materials, and energy recovery options instead of landfilling.
This shift helps cut costs while supporting circular economy goals and lowering environmental impact from waste disposal practices.
Lower rate for qualifying materials
Materials that create less pollution qualify for a lower tax rate at UK landfills. The current rate stands at £4.05 per tonne for specific waste types that meet strict testing standards.
These materials must pass the Loss on Ignition test, showing 10% or less LOI to receive the reduced rate since April 2016.
Inactive waste makes up most qualifying materials for the lower tax band. Local councils and waste operators need proper testing to prove their waste meets these standards. The testing helps sort active waste from inert materials like soil, rocks, and concrete.
This careful sorting leads to better waste management and lower costs for everyone.
Tax savings through proper waste sorting create real benefits for waste producers. Mixed loads often face higher standard rates unless they contain small amounts of qualifying materials.
Smart waste management practices help businesses save money while supporting sustainable practices. The lower rate pushes companies to separate their waste properly before disposal.
“Landfill Tax – Wikiwaste” from wikiwaste.org.uk and used with no modifications.
Exemptions and Reliefs for Landfill Tax
Landfill tax laws offer specific exemptions to help certain sectors manage their waste costs. These rules make waste disposal fair for special cases while still protecting our environment.
- Pet cemeteries get full tax relief on their waste disposal, making pet burials more affordable for grieving owners
- Mining and quarrying waste enjoys complete exemption from landfill tax because these industries produce large amounts of natural materials
- Dredged materials from waterways and harbours face no landfill tax charges, helping keep UK waters safe for boats
- Military forces visiting the UK receive exemptions on their waste disposal needs during their stay
- Drainage layers placed above landfill cell bases qualify for tax relief since they help control water flow
- Permanent caps used after disposal operations get tax breaks as they seal waste safely underground
- Companies can claim tax refunds if customers default on payments for waste services
- Businesses get tax relief when they move waste from one landfill site to another
- Tax refunds apply to landfilled materials later recycled or turned into energy through incineration
- Local councils receive tax breaks on waste that gets reused in other projects
- Quarry filling operations qualify for relief since they help restore land to its natural state
- Agricultural waste from farms often qualifies for lower rates or exemptions to support UK farming
Impact of Landfill Tax on Waste Management Practices
Tax exemptions lead to significant changes in waste handling methods across the UK. Many businesses now focus on recycling and resource recovery instead of sending waste to landfills.
The tax rates push companies to find better ways to deal with their waste materials. Local councils have started more recycling programs and waste sorting facilities. These changes help create a circular economy where materials stay useful longer.
The waste management sector has grown due to these tax rules. Companies invest in new technology to process waste differently. More jobs exist in recycling plants and energy-from-waste facilities.
The tax makes people think twice about throwing things away. UK businesses save money through smart waste choices like reusing materials or selling them to others. This shift helps the earth while creating new business chances.

Environmental and Economic Implications of Landfill Tax
Landfill tax creates strong benefits for both the environment and the UK economy. Local councils and businesses now send less waste to the 500 active landfill sites across Britain.
This tax pushes companies to find better ways to handle their rubbish through recycling and waste reduction. Many firms have started using energy-from-waste facilities instead of landfills, which helps create new jobs in the green sector.
Money from landfill tax goes straight into funding vital environmental projects. The revenue supports initiatives that make waste management more sustainable and eco-friendly. British businesses have changed their practices to avoid high disposal costs, leading to more recycling and less environmental damage.
These changes have sparked growth in the recycling industry while protecting natural resources for future generations.
Conclusion
The UK landfill tax system plays a vital role in waste reduction across Britain. Operators must pay these taxes while passing costs to waste producers through disposal fees. The tax rates push businesses toward greener waste solutions like recycling and reuse.
These clear rules and rates help create a cleaner future with less waste going to landfills.
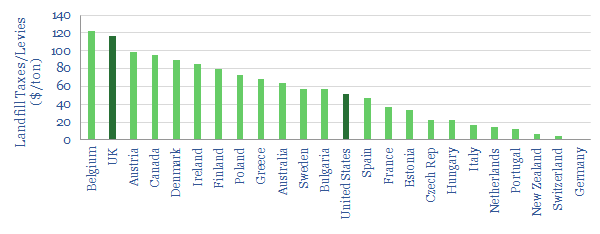
“Landfill costs: by country and over …” from thundersaidenergy.com and used with no modifications.
FAQs
1. Who must pay landfill tax in the UK?
Landfill operators, local councils, and waste management companies must pay landfill tax. This environmental tax applies to anyone disposing of waste at landfill sites.
2. What are the different rates for landfill tax?
The standard rate applies to active waste like household and medical waste. A lower rate exists for inactive waste such as soil and asphalt.
3. Does Scotland have different landfill tax rules?
Yes, Scottish landfill tax follows its own policies under the Scottish government, though rates often mirror those in the rest of the UK.
4. How does landfill tax support environmental projects?
Landfill tax revenue funds sustainable waste management and environmentally friendly initiatives. The money helps create energy-from-waste facilities and supports local waste reduction strategies.
5. Are there exemptions from landfill tax?
Some materials used for site restoration at landfills are exempt. The Welsh government and local authorities may also qualify for specific exemptions on certain types of waste disposal.
6. How does landfill tax affect council tax rates?
The cost of landfill tax influences council tax rates because local authorities must include waste management costs in their budgets. This encourages councils to focus on sustainable practices and proper handling of hazardous wastes.







