Here are five construction waste recycling methods through which sustainable builders achieve recycling and reuse of building waste in construction projects.
Depending on assumptions made about the disposal cost of demolition materials when pricing the work, it may be very easy to show a cost reduction. If the tender price allows for disposal to landfill, any alternative which costs less than the circa. £110/ tonne landfill gate fee (Landfill Tax + Landfill Company's tipping charge) saves the contractor money.
We made the following video, which is based upon this article, watch it now, but do please return for the additional detail in our article:
 Not only that, they simultaneously save themselves money through reduced building costs.
Not only that, they simultaneously save themselves money through reduced building costs.
- Segregating timber waste on site and sale for re-use
- Storing reusable bricks and roof tiles from demolition phase, for use in later phases
- Segregating metal waste on site
- Segregating paper and cardboard waste and bale on site prior to disposal
- Clean soil from excavation can be tested by ‘CLAIRE’ and then dealt with as Material Transfers
to be reused on another site.
Extracting value from demolition wood waste is no “walk-in-the-park” toward making money from demolition waste. To do so requires initial investigative work to seek out potential construction waste recycling methods which can provide a suitable materials. That's only the first step, because you won't be able to sell the recycled materials until suitable markets for the wood available from any one demolition project are found.
What might also be a profitable re-use will also depend upon how far the site is from a suitable buyer, due to transport costs. In fact we think that the best route will usually be to find a buyer first and then consider whether the material they will pay you for the material in your building before even starting to demolish it.
An Example Markets for Wood Waste
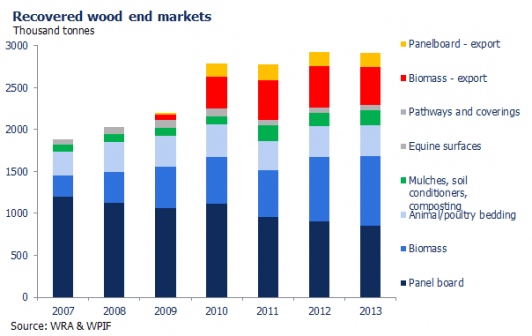
The markets for wood waste include use as feedstock for engineered woods, landscape mulch, soil conditioner, animal bedding, compost additive, sewage sludge bulking medium, and boiler fuel.
Construction Waste Recycling Methods
To bring in a net income benefit your construction waste recycling methods must be chosen to extract a salable quality and quantity of material from your building demolition materials.
An example is the first in our list (i.e. Wood Waste).
All the end markets for recovered wood have similar processing requirements in that the wood waste has to be separated from other wastes, cleaned by removing contaminants and fasteners, and processed through grinding or chipping before it can be sold. The final use of the wood waste generally determines how clean and consistent the construction waste recycling method must achieve.
Here are our 5 construction waste recycling methods:
1 – Segregating timber waste on site and sale for re-use
The most desirable option for wood waste management is to reuse the structural elements or reuse of architectural elements which include casings, banisters, and mouldings. Large timbers from older or unique structures can be salvaged and reused as structural elements in new buildings.
However, if lumber is to be reused as a structural element, it would need to be re-certified by a lumber inspector first. One option that may be potentially cost effective is the employment of firms that offer certified lumber inspectors that can grade lumber for use on site. via www.calrecycle.ca.gov
According to LetsRecycle:
“Traditionally, the largest outlet for clean, recycled woodchip has been the panel board industry, which uses the material in the production of chipboard. Reprocessed wood packaging – such as pallets – is also eligible for support under the Packaging Waste Recovery Note System (PRN).
However, an increasing number of wood recyclers are diversifying into “value-added” markets such as animal bedding, for which higher grade – clean and untreated – waste wood is allowed. Waste wood markets for equine surfacing, public pathway surfacing and garden mulches have also been steadily developing for grade ‘A’ waste wood.
Dedicated biomass plants – both at home and abroad – have also offered a growing market for recycled woodchip, as the government strives to generate more renewable energy and councils and waste management firms seek to divert lower-grade wood, which is not suitable for recycling, away from landfill.
However, a number of biomass plants due to take waste wood have either come online, or are expected to shortly, in Scotland and also in England. This has impacted on gate fees for waste wood, with greater demand for material leading to lower gate fees – or in some cases in Scotland and certain parts of the UK a payment being made.”
PAS 104 applies to wood recycling in the panelboard manufacturing industry. Specification for quality and guidance for good practice for the supply of post consumer wood for consumption in the manufactuer of panelboard products, ISBN 0-580-43531-8 WRAP and BSI, 2004.
During 2019 waste wood gate payments have improved markedly for high grade wood waste, according to the LetsRecycle.com database of prices.
The Market Price Available for Waste Wood
Low grade timber has little or no value, in fact the gate fee paid for wood ranges from £20 per tonne paid, to a fee of £20/tonne according to the LetsRecycle prices database.
However, think of wood delivered similar in shape and quality to that found in any standard pallet, and you begin to have a more salable proposition. That high a degree of selection, and consistency in the wood output for sale, would be considered to be “high grade” wood waste. “High grade” wood waste is worth the top end of the range and would be paid into the contractor's bank account, when transported to a biomass combustion plant gate.
The Importance of Grading in any Wood Based Construction Waste Recycling Method
A grading structure which aims to clarify for the first time what kinds of recovered wood are suitable for different end markets should be used as the core of your construction waste recycling method. One such grading method has been published by the Wood Recyclers' Association (WRA).
The four grades represent an important step towards developing the UK's first fully-fledged standard for recovered wood, which is set to be produced by the Waste & Resources Action Programme (WRAP), but requires more detail. via www.letsrecycle.com
A Grade is the highest value and highest quality of waste wood. This ‘clean' low moisture material consists of waste, cuttings and shavings from solid wood in its natural state, packing cases and pallets made from solid wood, and cable reels with nails and other metal removed during the process. The high quality of A Grade biomass means it is suitable for use by facilities that have not been specially licensed under the Industrial Emissions Directive. via stobartwoodfuel.com
It should be possible in most areas to find a buyer for wood which falls into the category of A Grade biomass.
If this material was costed as a waste for landfill disposal at tender, and it can be sold at £20/tonne, the saving on the tendered price per tonne may be as high as £110 + £20 = £130/tonne.
2 – Storing reusable bricks and roof tiles from demolition phase, for use in later phases
Many people prefer the beauty of old bricks and roof tiles for new construction.
There are many benefits to salvaging, cleaning and reusing old bricks from a dismantled brick wall. Many people like old bricks that have an aged appearance to add character to a new project. Of course, there are monetary savings in doing this, as well as the satisfaction of performing an environmentally friendly act. via sfgate.com
By collaborating with a local architectural antiques company it may be possible to negotiate a good price for the bricks and tiles from any specific demolition job. However, careful planning and programming is usually needed from an early stage of a project to allow time for the dismantling needed without delaying other areas of the construction project.
Another method of sale may be by auction on a website such as eBay.
3 – Segregating metal waste on site
Metal waste is generally categorized into Ferrous and Non-ferrous types. Prices paid do vary month by month but for iron scrap are in the range £100 and £150 per tonne.
According to the LetsRecycle.com prices data the value of non-ferrous demolition materials at the gate of a metal scrap dealer varies between £400 and £3,600 per tonne.
Reinforcing bars released during crushing operations are an asset if segregated and sold.
Prices are relatively high for metal scrap currently, and can easily go higher:
Non-ferrous scrap metal
• Copper dry bright wire prices fluctuated throughout the last months of the year Prices in early December stood at £4250per tonne, compared to £4525 per tonne at the start of the year.
• The price of aluminium pure cuttings has slowly declined throughout 2018. They are currently trading at £650 per tonne, having started the year at £800 per tonne
• 18/8 stainless solid prices also declined slightly throughout the last months of the year. They were trading at £615 per tonne in early December.
• Lead battery prices have fluctuated slightly and currently stand at £525 per tonne. They previously peaked at £600 per tonne in November 2016.
Ferrous scrap metal prices
• Prices for ferrous metal grades declined towards the end of the year. Prices declined to around £155 per tonne for OA Heavy grade, £135 per tonne for 4C grade, and £82.5 per tonne for grade 10. 7B grade saw prices rise to £117 per tonne. via WRAP (UK).
4 – Segregating paper and cardboard waste and bale on site prior to disposal
Construction waste includes a high proportion of packaging waste, especially during the fit-out stage. If this was sent to landfill it would cost over £100 per tonne in landfill disposal fees at the gate.
Unfortunately, due to the Chinese ban in 2018 against accepting imported waste segregating paper and cardboard produces only a nominal saving by selling baled paper and cardboard waste rather than landfilling it.
5 – Test Soil Using ‘CL:AIRE’ and if Satisfactory Avoid the Material Carted Off-Site Being Considered to be a Waste
Clean soil from excavation can be tested using ‘CL:AIRE’ methodology and then if satisfactory be dealt with as “Material Transfers to be reused on another site”.
CL:AIRE has produced methods to rationalize the redevelopment of land just as their methods can be used to verify the performance of innovative remediation technologies, it can also be used to demonstrate that a demolition site is clean land. That means that a sustainable alternative to disposing of waste in landfill sites is then possible.
Disposal by sale as topsoil is then possible without the automatic classification, which is normal for excess soil from demolition of old industrial sites, as a waste. Once a material is classed as a waste it's value is also removed. A satisfactory CL:AIRE test result can be of great value to a demolition contractor, opening new opportunities to use a variety of construction waste recycling methods, and create income from demolition materials.
Concluding : 5 Construction Waste Recycling Methods Which Save Building Costs
 We hope that our 5 construction waste recycling methods listed above which we think can save on constructor's building costs were useful. There are also very often also points to be awarded for sustainability when adopting these recycling methods.
We hope that our 5 construction waste recycling methods listed above which we think can save on constructor's building costs were useful. There are also very often also points to be awarded for sustainability when adopting these recycling methods.
With luck we hope to have given you some great ideas to achieve better recycling and reuse of building waste in your construction projects. There are many concepts for reuse and recycling of construction and demolition waste. These were just 5!
Above all, we hope we have alerted you to the need to:
- start thinking about construction waste recycling methods at a very early stage especially for building jobs which entail demolition
- look for local markets and select a suitable method to remove and segregate the materials which have value before demolition starts, because afterward the structure has been knocked down is often too late
- consider doing all this though the use of a suitable SWMP (Site Waste Management Plan) procedure.
Don't forget to watch our “5 Construction Waste Recycling Methods” video, if you have not seen it yet watch it here.






I prefer to do my own project concerning waste I am sure. I know recycling construction waste recycling can be a money saver. It can help me a lot.